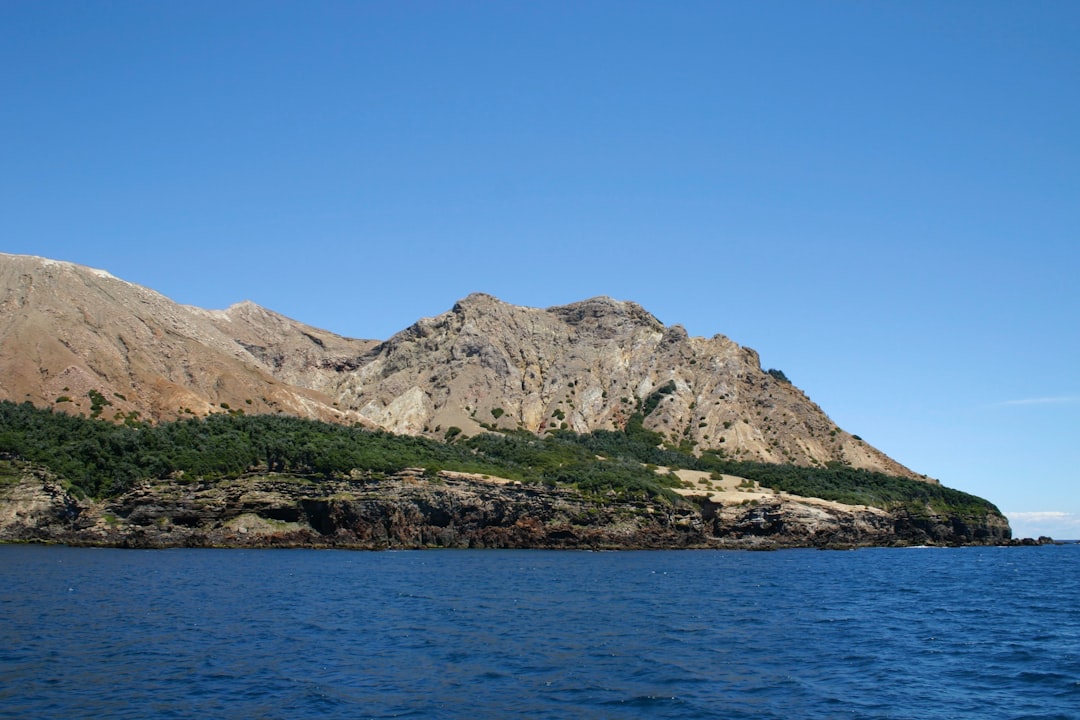
The Kola Peninsula, a prominent landform located in the northwestern part of Russia, is a region rich in geological diversity and historical significance. Bordered by the Barents Sea to the northwest and the White Sea to the southeast, this peninsula extends into the Arctic Circle, making it a unique area for both scientific study and natural beauty. The Kola Peninsula is characterized by its rugged terrain, which includes mountains, plateaus, and a variety of ecosystems that range from tundra to boreal forests.
Its geographical position not only influences its climate but also plays a crucial role in the geological processes that have shaped its landscape over millions of years. The Kola Peninsula is not just a geographical entity; it is a testament to the Earth’s dynamic history. The region has been a focal point for geological research due to its complex rock formations and mineral wealth.
The interplay of tectonic forces, glaciation, and volcanic activity has created a landscape that is both fascinating and challenging to study. As scientists continue to explore this remote area, they uncover insights into the Earth’s past, providing valuable information about plate tectonics, mineral resources, and environmental changes.
Key Takeaways
- The Kola Peninsula is located in northwest Russia and is known for its unique geological features and mineral resources.
- The geological history of the Kola Peninsula dates back to billions of years, with evidence of ancient rock formations and tectonic activity.
- The region is home to a variety of rock types and formations, including granite, gneiss, and sedimentary rocks, shaped by geological processes over time.
- Tectonic activity and plate movements have played a significant role in shaping the geology of the Kola Peninsula, leading to the formation of mountain ranges and fault lines.
- Glaciation has had a profound impact on the geology of the Kola Peninsula, shaping the landscape and contributing to the formation of mineral deposits.
Geological history of the Kola Peninsula
The geological history of the Kola Peninsula is a narrative that spans billions of years, marked by significant events that have shaped its current form. The oldest rocks in the region date back to the Precambrian era, approximately 3 billion years ago. These ancient formations are primarily composed of granites and gneisses, which provide evidence of the intense geological processes that occurred during the early stages of Earth’s development.
Over time, these rocks have been subjected to various metamorphic processes, resulting in a complex layering of minerals that tell a story of heat, pressure, and time. Throughout its history, the Kola Peninsula has experienced multiple phases of tectonic activity. The collision of tectonic plates has led to the formation of mountain ranges and deep valleys, while volcanic activity has contributed to the creation of unique rock types.
The region’s geological evolution has also been influenced by significant climatic changes, including periods of glaciation that have sculpted the landscape. Understanding this intricate history is essential for geologists as they piece together the events that have shaped not only the Kola Peninsula but also the broader geological framework of northern Europe.
Rock types and formations on the Kola Peninsula
The Kola Peninsula boasts an impressive array of rock types and geological formations that reflect its tumultuous history. Among the most prominent are the ancient crystalline rocks, which include granites, gneisses, and schists. These rocks are often found in the northern and central parts of the peninsula and are characterized by their high metamorphic grade.
The presence of these rocks indicates significant geological processes, including high temperatures and pressures that have transformed original sedimentary materials into more complex structures. In addition to crystalline rocks, the Kola Peninsula is home to various sedimentary formations that have developed over time. These include sandstones, shales, and limestones that were deposited in ancient marine environments.
The interplay between these sedimentary layers and the older crystalline rocks creates a fascinating geological tapestry that offers insights into past environmental conditions.
This diverse array of rock types not only enhances the scientific value of the Kola Peninsula but also contributes to its stunning natural landscapes.
Tectonic activity and plate movements in the region
| Plate Movement | Tectonic Activity |
|---|---|
| Convergent Boundary | Subduction zones, mountain building, volcanic activity |
| Divergent Boundary | Rift valleys, mid-ocean ridges, volcanic activity |
| Transform Boundary | Earthquakes, fault lines |
Tectonic activity plays a pivotal role in shaping the geology of the Kola Peninsula. The region is situated at the boundary of several tectonic plates, including the Eurasian Plate and smaller microplates that have influenced its geological development. The interactions between these plates have resulted in various geological phenomena, including earthquakes, mountain building, and volcanic activity.
The ongoing movements of these plates continue to affect the landscape, creating opportunities for further research into tectonic processes. The Kola Peninsula’s tectonic history is marked by significant events such as rifting and subduction. These processes have led to the formation of fault lines and fractures that can be observed throughout the region.
Geologists study these features to gain insights into past tectonic events and predict future movements. The understanding of tectonic activity in the Kola Peninsula not only contributes to local geological knowledge but also enhances global understanding of plate tectonics and their implications for Earth’s geology.
Impact of glaciation on the geology of the Kola Peninsula
Glaciation has had a profound impact on the geology of the Kola Peninsula, shaping its landscape in ways that are still evident today. During the last Ice Age, massive glaciers advanced across the region, carving out valleys and fjords while depositing sediments that would later become part of the geological record. The erosive power of these glaciers transformed rugged terrains into smooth surfaces, creating features such as drumlins and moraines that are characteristic of glaciated landscapes.
The effects of glaciation are not limited to physical alterations; they also influence soil composition and vegetation patterns in the region. As glaciers retreated, they left behind a mosaic of sediments that contributed to soil fertility in certain areas while creating barren landscapes in others. This variability has led to diverse ecosystems on the Kola Peninsula, ranging from lush forests to stark tundra.
Understanding how glaciation has shaped both the geology and ecology of this region is crucial for scientists studying climate change and its long-term effects on Earth’s systems.
Mineral resources and mining on the Kola Peninsula

The Kola Peninsula is renowned for its rich mineral resources, making it a significant area for mining activities. The region is particularly famous for its deposits of nickel, copper, palladium, and rare earth elements. These minerals are found in various geological formations throughout the peninsula, often associated with ultramafic rocks that have undergone extensive alteration processes.
The extraction of these resources has played a vital role in Russia’s economy and continues to attract interest from mining companies worldwide. Mining operations on the Kola Peninsula face unique challenges due to its remote location and harsh climate. However, advancements in technology have made it possible to extract valuable minerals while minimizing environmental impacts.
Sustainable mining practices are increasingly being adopted to ensure that resource extraction does not compromise the delicate ecosystems present in the region. As demand for minerals continues to rise globally, responsible mining practices will be essential for balancing economic growth with environmental stewardship on the Kola Peninsula.
Unique geological features of the Kola Peninsula
The Kola Peninsula is home to several unique geological features that set it apart from other regions. One notable example is the Kola Superdeep Borehole, which represents one of humanity’s deepest drilling projects into the Earth’s crust. This borehole provides invaluable data about subsurface geology and has yielded insights into rock formation processes at unprecedented depths.
The findings from this project have contributed significantly to our understanding of continental crust dynamics. Another remarkable feature is Lake Imandra, one of the largest lakes in the region, which was formed as a result of glacial activity. The lake’s basin showcases various sedimentary deposits that reveal information about past climatic conditions and glacial movements.
Additionally, the presence of unique mineral formations such as apatite-nepheline syenites adds to the geological diversity of the peninsula. These features not only enhance scientific knowledge but also attract geologists and tourists alike who seek to explore this captivating landscape.
Environmental concerns and conservation efforts in the region
As industrial activities expand on the Kola Peninsula, environmental concerns have emerged regarding the impact on local ecosystems and communities. Mining operations pose risks such as habitat destruction, water pollution, and soil degradation. The delicate balance between resource extraction and environmental preservation is a pressing issue that requires careful management and regulation.
In response to these challenges, various conservation efforts have been initiated to protect the unique ecosystems found on the Kola Peninsula. Environmental organizations work alongside government agencies to promote sustainable practices in mining and land use. Initiatives aimed at restoring damaged habitats and preserving biodiversity are crucial for maintaining ecological integrity in this region.
By fostering awareness about environmental issues and promoting responsible resource management, stakeholders hope to ensure that future generations can enjoy both the natural beauty and geological significance of the Kola Peninsula.
Geological research and studies conducted on the Kola Peninsula
The Kola Peninsula has long been a focal point for geological research due to its diverse rock formations and complex geological history. Numerous studies have been conducted by both Russian and international scientists seeking to understand various aspects of its geology. Research topics range from examining ancient rock formations to investigating modern tectonic activity and mineral resources.
One significant area of study involves understanding how glaciation has influenced both geology and ecology in the region. Researchers analyze sediment cores from lakes and rivers to reconstruct past environments and assess how climate change may impact future conditions. Additionally, ongoing studies related to mineral exploration aim to identify new deposits while ensuring sustainable practices are implemented during extraction processes.
The wealth of knowledge gained from these research efforts contributes not only to local understanding but also enhances global geological science.
Geological significance of the Kola Peninsula in the context of global geology
The geological significance of the Kola Peninsula extends far beyond its borders; it serves as a critical reference point for understanding global geological processes. Its unique combination of ancient rock formations, tectonic activity, glaciation effects, and mineral resources provides valuable insights into Earth’s history and dynamics. Geologists often use data from this region to draw parallels with other areas around the world experiencing similar geological phenomena.
Moreover, studies conducted on the Kola Peninsula contribute to broader discussions about plate tectonics, mineral resource management, and climate change adaptation strategies globally. As researchers continue to explore this fascinating region, they uncover new information that enhances our understanding of Earth’s complex systems while addressing pressing environmental challenges faced by many regions worldwide.
Future prospects for geological exploration and understanding on the Kola Peninsula
Looking ahead, there are promising prospects for further geological exploration on the Kola Peninsula. Advances in technology are enabling scientists to conduct more detailed studies than ever before, allowing for deeper insights into subsurface geology and mineral deposits. As interest in sustainable resource management grows globally, there will likely be increased investment in research aimed at balancing economic development with environmental protection.
Additionally, interdisciplinary approaches combining geology with ecology will be essential for understanding how human activities impact natural systems on the peninsula. Collaborative efforts among scientists from various fields can lead to innovative solutions that address both resource needs and conservation goals. As exploration continues on this remarkable landform, it holds great potential for enhancing knowledge about Earth’s past while informing sustainable practices for its future.
The Kola Peninsula, located in the far northwest of Russia, is a region of significant geological interest due to its unique mineral compositions and ancient rock formations. A related article that delves into the fascinating geology of this area can be found on the Hey Did You Know This website. This article provides insights into the peninsula’s rich geological history and the various scientific studies conducted there. For more detailed information, you can read the full article by visiting this link.
FAQs
What is the geology of the Kola Peninsula?
The Kola Peninsula is located in the far northwest of Russia and is known for its diverse and unique geology. It is characterized by ancient rocks, including some of the oldest on Earth, as well as a variety of mineral deposits.
What are the main rock types found on the Kola Peninsula?
The Kola Peninsula is composed of a wide range of rock types, including ancient crystalline rocks such as gneiss, granite, and schist, as well as sedimentary rocks like limestone and shale. The region also contains significant deposits of apatite, a phosphate mineral used in fertilizer production.
What are the geological features of the Kola Peninsula?
The Kola Peninsula is home to a number of unique geological features, including the Khibiny and Lovozero massifs, which are large igneous intrusions that contain a variety of rare minerals. The region also features numerous lakes, rivers, and fjords, which were formed by glacial activity during the last Ice Age.
What is the significance of the geology of the Kola Peninsula?
The geology of the Kola Peninsula is of great scientific interest due to its ancient rocks and unique mineral deposits. It provides valuable insights into the Earth’s early history and the processes that have shaped the planet over billions of years. Additionally, the region’s mineral wealth has made it an important area for mining and resource extraction.
